The Anatomy of Lubricant Analysis Report: How to Read and Use Your Reports Effectively
Oil and grease analysis reports are essential tools in maintenance and reliability programs for industrial machinery, automotive fleets, and other lubricated equipment.
These reports provide valuable insights into the condition of both the lubricant and the machinery, helping to predict failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and extend equipment life. This article explores the anatomy of a lubricating oil or grease analysis report, detailing each section and its significance.
Severity Indicators
Severity Indicators provide a quick overview of the condition of both the lubricant and the equipment based on the analysis results.
Labs may use different systems to convey severity, such as traffic lights or numerical ratings. A traffic light system uses colors—green for normal, yellow for caution, and red for critical—to highlight the urgency of action required. Alternatively, a numerical scale, often ranging from 0 to 4 or 1 to 3, is combined with these colors to indicate the severity level more precisely.
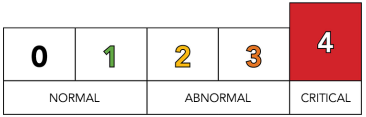 |
| Severity Indicators for Polaris Lab Reports |
These indicators are vital as they help maintenance teams quickly assess which issues need immediate attention and which can be monitored over time. By understanding the severity flags, users can better prioritize maintenance actions to prevent failures and optimize equipment performance.
Account Information
The Account Information section includes all relevant customer details, such as the company name, account number, contact person, phone number, and address. This section is important for accurately linking the report to the correct customer, facilitating easy management and reference of analysis results within their maintenance processes.
Component Information
Component Information focuses on the machinery or equipment from which the sample was drawn. It generally covers details such as the component ID, component type, make and model of the equipment, and operating hours or mileage.
Accurate component information is crucial as it provides context for the analysis, allowing for more precise interpretation of the results.
Understanding the specific equipment type and its operational context helps in diagnosing potential issues and tailoring maintenance recommendations accordingly.
Sample Information
The Sample Information section outlines the key details of the lubricant sample submitted for analysis. It typically includes the sample ID, the type of lubricant and its grade, the date of collection, and the method used for sampling—whether from a drain plug, sample valve, or vacuum pump.
Additionally, this section provides information on the sampling location, indicating the exact point within the equipment or system where the sample was taken, as well as the analytical slate, which specifies the tests to be conducted on the sample.
Accurate and thorough sample information is crucial for ensuring the validity and reliability of the analysis, as improper sampling methods or incomplete details can lead to misleading results, ultimately impacting maintenance strategies and decision-making.
Miscellaneous Information
This section provides comprehensive details that impact lubricant performance and the overall condition of the equipment. It includes information on the filters used, specifying the filter type, micron rating, and potentially the last replacement date.
Understanding the filter type and its condition is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of contamination control measures and determining if the filters are adequately protecting the equipment by maintaining lubricant cleanliness.
In addition to filter details, this section covers recent maintenance activities that might influence lubricant performance, such as repairs, overhauls, or equipment adjustments. It also provides relevant environmental and operating conditions—such as ambient temperature, humidity, load, speed, and operating temperatures—that can affect lubricant behavior and equipment wear.
Information about the lubricant itself, including its type, brand, viscosity, and any additives, is also included to offer context for analysis. By capturing this range of information, the report enables a more accurate interpretation of analysis results and helps in identifying the root causes of potential issues, ensuring informed maintenance decisions are made.
 |
| Filter Information, Miscellaneous Information and Product Information for Polaris Lab Report |
Results Interpretation and Diagnosis
The Comment or Diagnosis section is one of the most critical parts of the report, where analysts provide their expert interpretation of the results.
It includes a summary of findings that identifies potential issues, such as contamination, wear, or degradation of the lubricant, and offers actionable recommendations, such as changing the lubricant, adjusting maintenance schedules, or addressing specific mechanical problems.
This section distills the raw data into practical guidance, making it one of the most valuable parts of the report for decision-making.
 |
| Results Interpretation and Diagnosis for Polaris Lab Report |
Analytical Results
The Analytical Results section is the core of the report, presenting the actual test results. It typically includes a list of tests performed (such as viscosity, acid number, water content, particle count, and elemental analysis), the numerical values obtained from each test, the units of measure (e.g., cSt for viscosity, ppm for contaminants), and references to the standards followed (such as ASTM, ISO, or manufacturer specifications).
Additionally, it provides the range of normal results for comparison. These analytical results offer the empirical data needed to evaluate the condition of the lubricant and equipment, providing a solid foundation for maintenance decisions.
 |
| Part of Analysis Results Section for Polaris Lab Report |
Supportive Graphs, Charts, Images and Trend Analysis
Graphs, Charts, and Trend Analysis are often included to enhance the understanding of the data. Graphs can plot key parameters over time, such as wear metals, viscosity, or contamination levels, while charts summarize test results visually, making it easier to spot trends or anomalies.
Trend analysis involves examining historical data to identify patterns or predict future issues, providing valuable foresight that can be used to prevent failures and optimize maintenance schedules.
Visual representation of data helps in quickly assessing the condition of the lubricant and equipment, allowing for proactive maintenance decisions.
In some cases, the report may include Images from Analytical Techniques, such as Analytical Ferrography, Membrane Patch Colorimetry, or Blotter Spot Tests. These images provide additional insights into the condition of the lubricant and the machinery.
For example, analytical ferrography images can show the size, shape, and composition of wear particles, which helps in identifying specific wear mechanisms.
Membrane patch colorimetry images provide a visual assessment of lubricant contamination levels, while blotter spot tests offer a quick overview of the lubricant’s cleanliness and oxidation state.
These visual aids complement the quantitative data, providing a more complete and intuitive understanding of the lubricant condition.
 |
| Example of trend graph from Polaris Lab Report |
Disclaimer and Responsibility Limitation
The Disclaimer section is typically the final part of the report. It outlines the limitations of the analysis, stating that results are based on the specific sample provided and may not represent the entire lubricant batch or the overall condition of the equipment.
It also includes liability clauses that limit the laboratory's responsibility, emphasizing that maintenance decisions remain the responsibility of the equipment owner.
This section ensures that the report is used appropriately and clarifies the boundaries of the analysis service, helping to manage expectations and guide the use of the information provided.
In conclusion, a comprehensive lubricating oil or grease analysis report is a valuable tool for maintaining the reliability and efficiency of machinery.
By understanding each section of the report, from account information to trend analysis and visual assessments, stakeholders can make informed decisions that enhance equipment performance and extend its lifespan.
Regular analysis and careful interpretation of these reports form the backbone of an effective predictive maintenance program, ultimately reducing downtime and operational costs.







